Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the airways in the lungs become inflamed and narrow, leading to difficulty breathing. Understanding asthma’s causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for managing the condition and improving your quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore these aspects in detail.

Causes of Asthma
Asthma is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While the exact cause of asthma is not entirely understood, several factors are known to trigger or worsen the condition.
Genetics
A family history of asthma or other allergic conditions, such as eczema or hay fever, increases the likelihood of developing asthma. Certain genes are linked to an increased risk of asthma, making it a hereditary condition.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold, can trigger asthma symptoms. Air pollution, cigarette smoke, and chemical fumes are also known to exacerbate asthma. In some cases, early exposure to certain environmental factors, such as tobacco smoke or air pollutants, may increase the risk of developing asthma later in life.
Respiratory Infections
Viral respiratory infections, particularly in early childhood, can lead to the development of asthma. These infections can cause long-term changes in the airways, making them more sensitive to asthma triggers.
Occupational Factors
Some people develop asthma due to exposure to certain substances in their workplace. This is known as occupational asthma and can be caused by inhaling fumes, gases, dust, or other harmful substances.
Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms can vary from person to person and may range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
1. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing is a hallmark symptom of asthma. This can range from mild breathlessness to severe shortness of breath during an asthma attack.
2. Wheezing: Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs when breathing, particularly during exhalation. It is caused by the narrowing of the airways and is a common symptom of asthma.
3. Coughing: Persistent coughing, especially at night or early in the morning, is a common asthma symptom. The cough may be dry or produce mucus.
4. Chest Tightness: People with asthma often experience a feeling of tightness or pressure in the chest, which can be uncomfortable and lead to anxiety.
5. Difficulty Sleeping: Asthma symptoms, particularly coughing and shortness of breath, can interfere with sleep, leading to fatigue and reduced quality of life.
6. Asthma Attacks: During an asthma attack, symptoms can worsen suddenly and severely. The airways become significantly inflamed and narrowed, making it extremely difficult to breathe. This can be a life-threatening situation requiring immediate medical attention.
Treatments for Asthma
While there is no cure for asthma, it can be effectively managed with a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and avoidance of triggers. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual’s specific needs and severity of the condition.
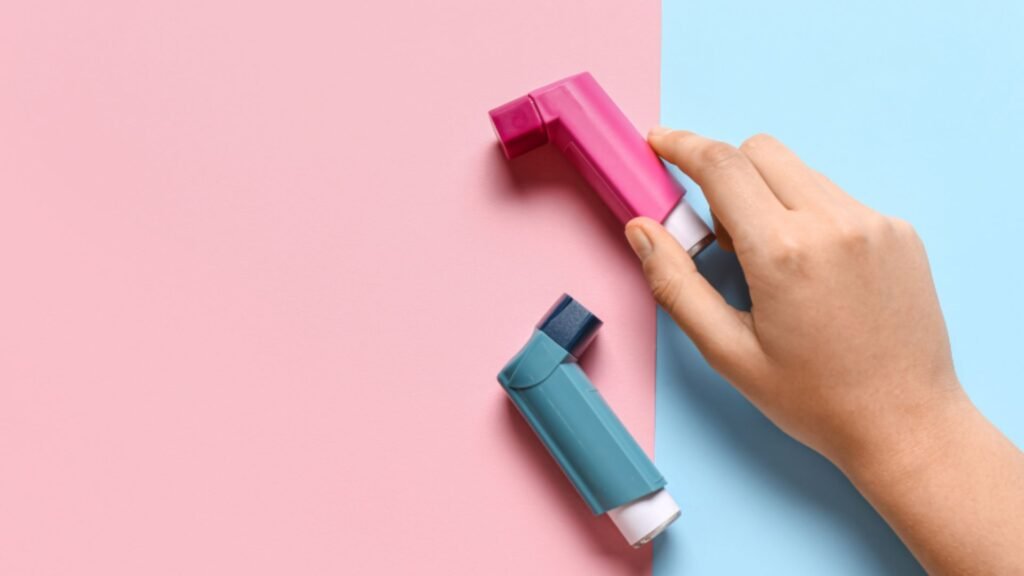
Inhalers
Inhalers are the most common treatment for asthma. They deliver medication directly to the lungs, helping to open the airways and reduce inflammation. There are two main types of inhalers:
– Reliever Inhalers: These are used during an asthma attack or when symptoms worsen. They contain fast-acting bronchodilators that quickly open the airways, making it easier to breathe.
– Preventer Inhalers: These are used daily to reduce inflammation in the airways and prevent asthma symptoms from occurring. They contain corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory medications.
Long-Acting Bronchodilators
These medications are taken regularly to help keep the airways open and prevent asthma symptoms. They are often used in combination with inhaled corticosteroids.
Leukotriene Modifiers
These oral medications help prevent asthma symptoms by blocking the action of leukotrienes, chemicals in the body that cause airway inflammation.
Biologic Therapies
For severe asthma that doesn’t respond to standard treatments, biologic therapies may be used. These are injections that target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process.
Lifestyle Changes
Managing asthma involves more than just taking medication. Avoiding triggers, such as allergens and irritants, is crucial. Regular exercise can help strengthen the lungs and improve overall health, but it should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Asthma Action Plan
Working with a healthcare provider to develop an asthma action plan is essential. This plan outlines how to manage symptoms daily, what to do if symptoms worsen, and when to seek emergency care.
Conclusion
Asthma is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, but with the right treatment plan and lifestyle adjustments, people with asthma can lead healthy and active lives. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following the recommended treatments can help you take control of your asthma and reduce the impact it has on your daily life. If you suspect you have asthma or your symptoms are worsening, consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.