Breast health is a vital aspect of overall well-being for women. Understanding how to maintain healthy breasts, recognize potential issues, and know when to seek medical advice can significantly impact your health. Here’s a comprehensive guide to breast health, including preventive measures, common issues, and essential self-care tips.

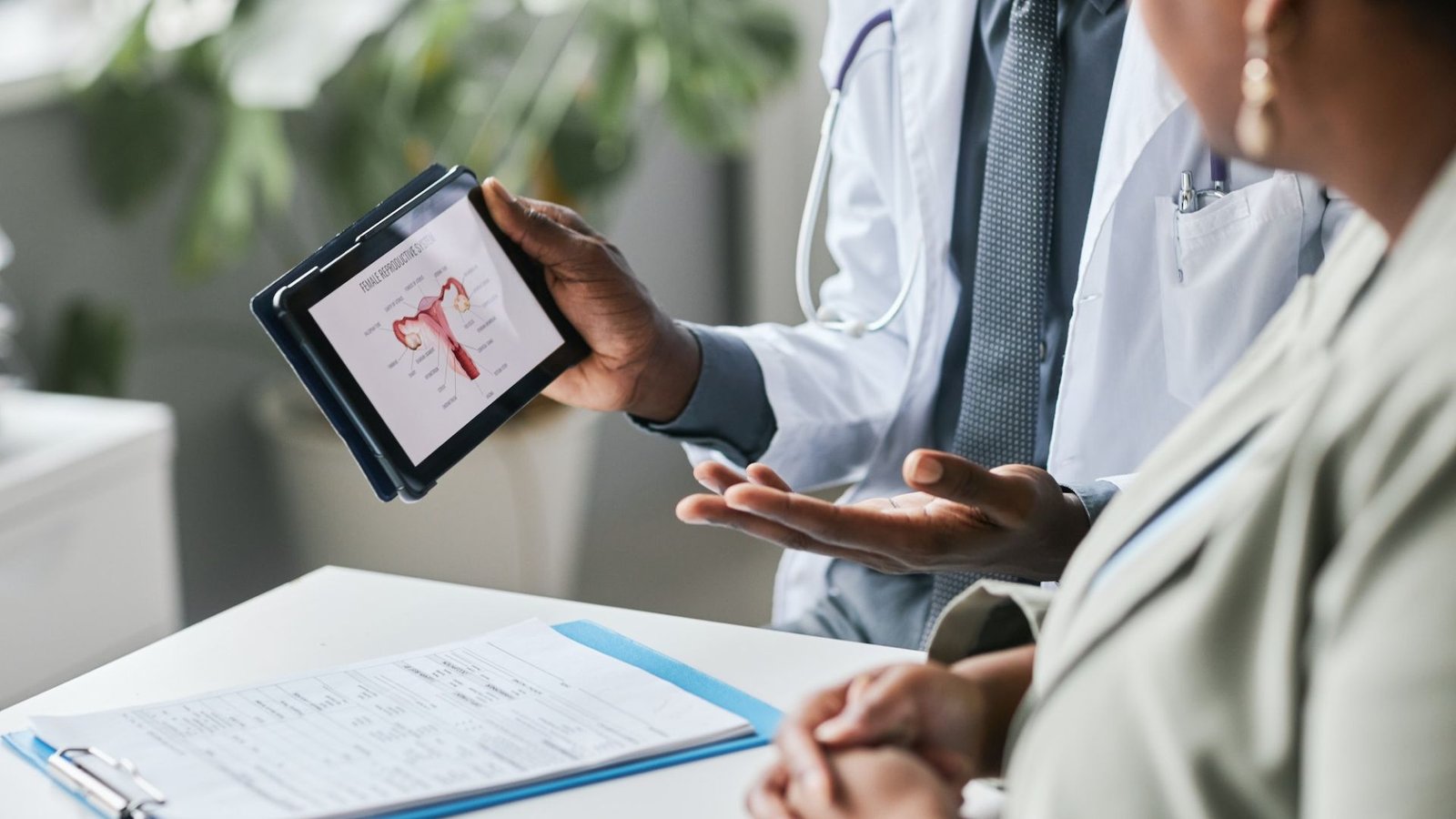
Understanding Breast Anatomy and Function
Breasts are complex structures composed of glandular tissue, fatty tissue, connective tissue, and lymph nodes. They are primarily responsible for producing milk in females, but their health is crucial for overall well-being.
- Glandular Tissue: Includes lobules, which produce milk, and ducts, which transport milk to the nipple.
- Fatty Tissue: Provides support and protection to the glandular tissue.
- Connective Tissue: Includes ligaments that support the breast and keep it in place.
- Lymph Nodes: Part of the lymphatic system, which helps filter harmful substances and fight infections.
Importance of Regular Breast Self-Exams
Regular breast self-exams are an important practice for early detection of potential issues. Performing self-exams can help you become familiar with the normal look and feel of your breasts, making it easier to identify any changes.
How to Perform a Breast Self-Exam:
- Visual Inspection: Stand in front of a mirror with your shoulders straight and your arms at your sides. Look for any changes in size, shape, or contour of your breasts.
- Palpation: Using the pads of your fingers, gently press down on your breasts while lying down or standing up. Check for any lumps, bumps, or changes in texture.
- Nipple Check: Gently squeeze each nipple to check for any discharge or changes.
Understanding Common Breast Health Issues
Several conditions can affect breast health, ranging from benign issues to more serious concerns. Being aware of these conditions helps in early detection and treatment.
- Benign Conditions: These include fibrocystic breasts (lumpy or tender areas), breast cysts, and benign tumors such as fibroadenomas. These conditions are generally non-cancerous but should be monitored.
- Breast Cancer: A serious condition where malignant cells form in the breast tissue. Early detection through self-exams, clinical exams, and mammograms is crucial for effective treatment.
- Infections and Inflammations: Conditions like mastitis (infection of the breast tissue) or inflammation can cause pain, redness, and swelling. These require medical attention and treatment.
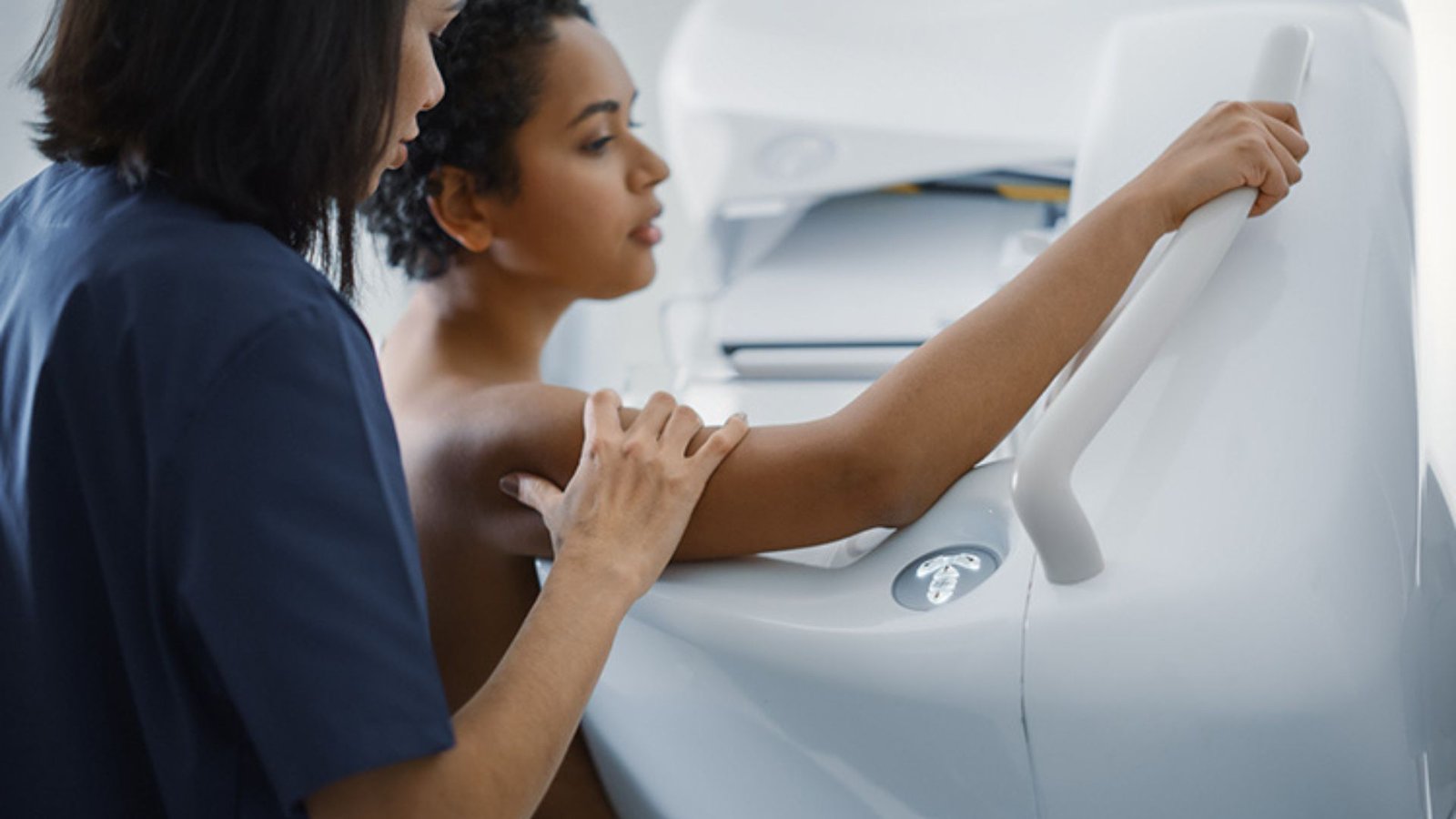
Screening and Diagnostic Tests
Regular screening and diagnostic tests are essential for early detection and monitoring of breast health issues.
- Mammograms: Recommended for women over 40 or those with a family history of breast cancer. Mammograms use X-rays to detect abnormalities in breast tissue.
- Ultrasound: Often used in conjunction with mammograms to provide a clearer view of breast tissue and identify cysts or other abnormalities.
- Biopsy: If a suspicious area is found, a biopsy may be performed to analyze the tissue for cancerous cells.
Healthy Lifestyle Practices for Breast Health
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices can support overall breast health and reduce the risk of breast-related issues.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, sugars, and high-fat diets.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of breast cancer.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any changes or concerns related to your breast health. Seek medical advice if you experience:
- New or Persistent Lumps: Any new lump or mass that does not go away or changes over time should be evaluated.
- Unexplained Discharge: Any discharge from the nipple, especially if it is bloody or occurs without squeezing.
- Persistent Pain: Pain that doesn’t go away or is associated with other symptoms like swelling or redness.
- Changes in Skin or Nipple: Any changes in the skin texture, color, or appearance of the nipple, including dimpling or puckering.
Conclusion
Maintaining breast health involves a combination of regular self-exams, routine screenings, and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Understanding the anatomy of the breast, recognizing common issues, and staying vigilant about any changes are key to managing breast health effectively. By incorporating these practices into your routine and seeking timely medical advice, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining your overall well-being and addressing any potential concerns.