The link between nutrition and cancer has been extensively studied, revealing that certain foods can play a significant role in both preventing cancer and aiding in recovery. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can strengthen the immune system, reduce inflammation, and support the body during and after cancer treatment. Here’s an overview of how nutrition impacts cancer prevention and recovery, and which foods are particularly beneficial.

The Role of Nutrition in Cancer Prevention
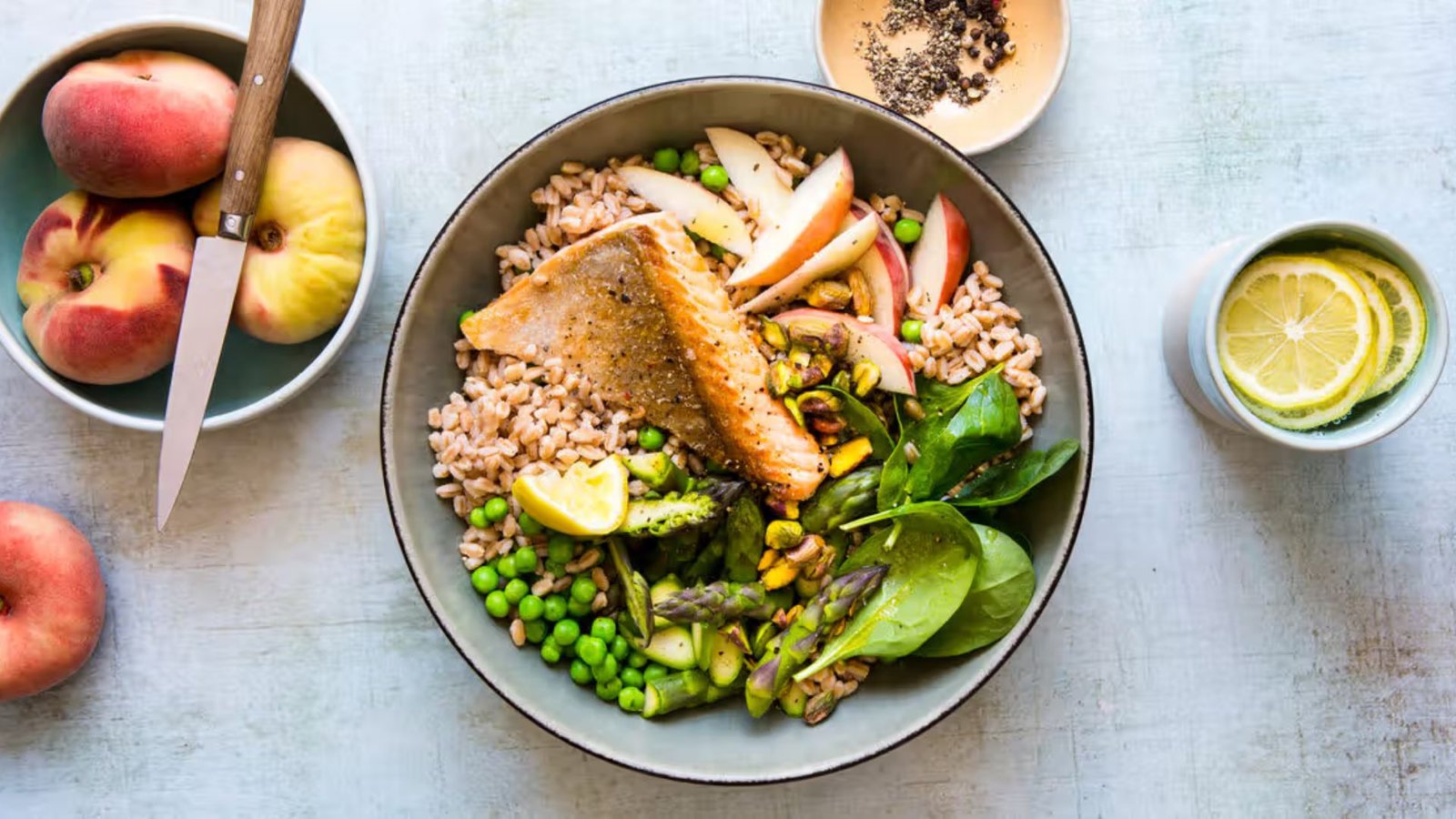
A diet rich in whole foods, particularly fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, is associated with a lower risk of developing certain types of cancer. These foods are packed with nutrients that help the body combat oxidative stress, a major contributor to cancer development.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to cancer. Fruits like berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries) are particularly high in antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and flavonoids. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale are also excellent sources of antioxidants, along with other vitamins and minerals essential for overall health.
Fiber-Rich Foods
A diet high in fiber has been linked to a reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables provide dietary fiber that aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight, another factor in cancer prevention. Fiber also promotes regular bowel movements, reducing the time potential carcinogens spend in the digestive tract.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage, contain compounds like sulforaphane that have been shown to inhibit cancer cell growth. These vegetables are also rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them a staple in a cancer-preventive diet.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce the risk of cancer. Chronic inflammation is linked to various types of cancer, and incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet can help mitigate this risk.
Nutritional Support During Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment can be physically and emotionally demanding, and proper nutrition is crucial to support the body during this challenging time. Maintaining a balanced diet can help manage side effects, boost energy levels, and improve overall well-being.
Protein-Rich Foods
Protein is essential for repairing tissues and maintaining muscle mass, especially during cancer treatment when the body is under stress. Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, and tofu are excellent sources of protein. For those with difficulty eating solid foods, protein shakes and smoothies can be a helpful alternative.
Hydrating Foods
Staying hydrated is vital, particularly for patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation, which can cause dehydration. In addition to drinking plenty of water, consuming hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and citrus fruits can help maintain hydration levels.
Soft and Easily Digestible Foods
Cancer treatments can cause side effects like mouth sores, nausea, and digestive issues. Soft and easily digestible foods like oatmeal, mashed potatoes, yogurt, and smoothies can provide necessary nutrients without irritating the digestive system. Incorporating ginger and peppermint can also help alleviate nausea.
Antiemetic Foods
Certain foods can help combat nausea, a common side effect of cancer treatment. Ginger, for example, has natural anti-nausea properties and can be consumed as tea, in smoothies, or added to meals. Peppermint tea and crackers are also soothing options that can help settle the stomach.
Post-Treatment Recovery and Long-Term Nutrition
After completing cancer treatment, maintaining a healthy diet is essential for recovery and long-term health. A focus on rebuilding strength, supporting the immune system, and preventing recurrence should guide nutritional choices.
Rebuilding with Whole Foods
A diet centered around whole foods, including a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, provides the necessary nutrients for recovery. Foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties should continue to be a key part of the diet to support ongoing health.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Post-treatment, it’s important to maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence. This can be achieved by balancing calorie intake with regular physical activity and focusing on nutrient-dense foods rather than empty calories.
Continued Hydration
Hydration remains crucial even after treatment, as it aids in digestion, circulation, and the elimination of toxins. Consuming a combination of water, herbal teas, and hydrating foods can help keep the body functioning optimally.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a critical role in both preventing cancer and supporting the body during and after treatment. By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods, fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and adequate protein into your diet, you can help protect your health and promote recovery. It’s important to work with healthcare professionals to tailor a nutrition plan that meets individual needs and supports overall well-being. As research continues to evolve, the connection between diet and cancer will become even clearer, emphasizing the importance of making informed dietary choices.